Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
谷口 良徳; 三原 武; 垣内 一雄; 宇田川 豊
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 195, p.110144_1 - 110144_11, 2024/01
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A reactivity-initiated accident (RIA)-simulated test CN-1 on a high-burnup 64 GWd/t mixed-oxide fuel rod sheathed with M5 cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor, resulting in fuel failure. A small opening with slight ballooning deformation characterized the post-test visual appearance of the test fuel rod. Simulation using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8/RANNS predicted rod survival under early phase loading induced by pellet-cladding mechanical interaction and subsequent boiling transition, and the cladding surface temperature measured online confirmed the occurrence of boiling transition. The experimental observation and simulation indicate that the failure was caused by a high-temperature rupture following increased rod-internal pressure. The RANNS sensitivity analysis revealed that a mechanical state parameter dedicated to predicting plastic instability might be an effective index for evaluating the risk of rupture failure during RIAs.
cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor, resulting in fuel failure. A small opening with slight ballooning deformation characterized the post-test visual appearance of the test fuel rod. Simulation using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8/RANNS predicted rod survival under early phase loading induced by pellet-cladding mechanical interaction and subsequent boiling transition, and the cladding surface temperature measured online confirmed the occurrence of boiling transition. The experimental observation and simulation indicate that the failure was caused by a high-temperature rupture following increased rod-internal pressure. The RANNS sensitivity analysis revealed that a mechanical state parameter dedicated to predicting plastic instability might be an effective index for evaluating the risk of rupture failure during RIAs.
成川 隆文; 近藤 啓悦; 藤村 由希; 垣内 一雄; 宇田川 豊; 根本 義之
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 582, p.154467_1 - 154467_12, 2023/08
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:94.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To evaluate the behavior of an oxide-dispersion-strengthened FeCrAl (FeCrAl-ODS) cladding tube under loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) conditions of light-water reactors (LWRs), the following two laboratory-scale LOCA-simulated tests were performed: the burst and integral thermal shock tests. Four burst and three integral thermal shock tests were performed on unirradiated, stress-relieved FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube specimens, simulating ballooning and rupture, oxidation, and quenching, which were postulated during a LOCA. The burst temperature of the FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube was 200-300 K higher than that of the Zircaloy cladding tube, and the FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube's maximum circumferential strain was smaller than or equal to the Zircaloy-4 cladding tube. These results indicate that the FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube has higher strength at high temperatures than the conventional Zircaloy cladding tube. The FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube did not fracture after being subjected to an axial restraint load of  5000 N, which is more than 10 times higher than the axial restraint load estimated for existing LWRs, during quenching, following isothermal oxidation at 1473 K for 1 h. The FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube was hardly oxidized during this isothermal oxidation condition. However, it melted after a short oxidation at 1673 K and fractured after abnormal oxidation at 1573 K for 1 h. Based on these results, the FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube should not fracture in the time range expected during LOCAs below 1473 K, where no melting or abnormal oxidation occurs.
5000 N, which is more than 10 times higher than the axial restraint load estimated for existing LWRs, during quenching, following isothermal oxidation at 1473 K for 1 h. The FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube was hardly oxidized during this isothermal oxidation condition. However, it melted after a short oxidation at 1673 K and fractured after abnormal oxidation at 1573 K for 1 h. Based on these results, the FeCrAl-ODS cladding tube should not fracture in the time range expected during LOCAs below 1473 K, where no melting or abnormal oxidation occurs.
 17 type PWR fuel cladding tube under LOCA-simulated burst conditions
17 type PWR fuel cladding tube under LOCA-simulated burst conditions古本 健一郎; 宇田川 豊
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(5), p.500 - 511, 2023/05
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to contribute to better modeling and evaluation of fuel fragmentation, relocation, and dispersal expected under loss of coolant accident (LOCA) conditions, LOCA-simulated cladding burst experiments were performed on as-received nonirradiated 17  17 type Zircaloy-4 cladding specimens that were internally pressurized. The experiments were designed to terminate at burst occurrence to focus on ballooning and rupture opening formation and to investigate the effects of various factors. The postburst cladding hoop strain decreased with the increase in azimuthal temperature distribution (ATD) of the cladding, as found previously. The rupture opening size increased with the increase in ATD and the increase in energy of the pressurized gas stored inside the pressure boundary of the test sample system. Comparison with the existing database, which included tests on irradiated rods containing fuel pellets, suggested that formation of the rupture opening was influenced by the characteristic behavior of high burnup fuels, such as limited gas migration in the cladding tube due to fuel-cladding bonding and interaction of the ejected fuel fragments with the cladding tube.
17 type Zircaloy-4 cladding specimens that were internally pressurized. The experiments were designed to terminate at burst occurrence to focus on ballooning and rupture opening formation and to investigate the effects of various factors. The postburst cladding hoop strain decreased with the increase in azimuthal temperature distribution (ATD) of the cladding, as found previously. The rupture opening size increased with the increase in ATD and the increase in energy of the pressurized gas stored inside the pressure boundary of the test sample system. Comparison with the existing database, which included tests on irradiated rods containing fuel pellets, suggested that formation of the rupture opening was influenced by the characteristic behavior of high burnup fuels, such as limited gas migration in the cladding tube due to fuel-cladding bonding and interaction of the ejected fuel fragments with the cladding tube.
成川 隆文; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(1), p.68 - 78, 2020/01
被引用回数:2 パーセンタイル:21.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)To evaluate the fracture limit of high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes under loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA) conditions, laboratory-scale integral thermal shock tests were performed using the following advanced fuel cladding tubes with burnups of 73 - 85 GWd/t: M-MDA , low-tin ZIRLO
, low-tin ZIRLO , M5
, M5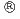 , and Zircaloy-2 (LK3). In total eight integral thermal shock tests were performed for these specimens, simulating LOCA conditions including ballooning and rupture, oxidation, hydriding, and quenching. During the tests, the specimens were oxidized to 10% - 30% equivalent cladding reacted (ECR) at approximately 1473 K and were quenched under axial restraint load of approximately 520 - 530 N. The effects of burnup extension and use of the advanced fuel cladding tubes on the ballooning and rupture, oxidation, and hydriding under LOCA conditions were inconsiderable. Further, the high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tube specimens did not fracture in the ECR values equal to or lower than the fracture limits of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tube reported in previous studies. Therefore, it can be concluded that the fracture limit of fuel cladding tubes is not significantly reduced by extending the burnup to approximately 85 GWd/t and using the advanced fuel cladding tubes, though it slightly decreases with increasing initial hydrogen concentration.
, and Zircaloy-2 (LK3). In total eight integral thermal shock tests were performed for these specimens, simulating LOCA conditions including ballooning and rupture, oxidation, hydriding, and quenching. During the tests, the specimens were oxidized to 10% - 30% equivalent cladding reacted (ECR) at approximately 1473 K and were quenched under axial restraint load of approximately 520 - 530 N. The effects of burnup extension and use of the advanced fuel cladding tubes on the ballooning and rupture, oxidation, and hydriding under LOCA conditions were inconsiderable. Further, the high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tube specimens did not fracture in the ECR values equal to or lower than the fracture limits of the unirradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tube reported in previous studies. Therefore, it can be concluded that the fracture limit of fuel cladding tubes is not significantly reduced by extending the burnup to approximately 85 GWd/t and using the advanced fuel cladding tubes, though it slightly decreases with increasing initial hydrogen concentration.
谷口 良徳; 宇田川 豊; 三原 武; 天谷 政樹; 垣内 一雄
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference / Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance Conference (Global/Top Fuel 2019) (USB Flash Drive), p.551 - 558, 2019/09
A pulse-irradiation test CN-1 on a high-burnup MOX fuel with M5 cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Although the transient signals obtained during the pulse-irradiation test did not show any signs of the occurrence of PCMI failure, the failure of the test fuel rod was confirmed from the visual inspection carried out after test CN-1. Analyses using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8 and RANNS were also performed in order to investigate the fuel behavior during normal operation and pulse-irradiation regarding the test fuel rod of CN-1, and the results were consistent with this observation result. These experimental and calculation results suggested that the failure of test fuel rod of CN-1 was not caused by hydride-assisted PCMI but high-temperature rupture following the increase in rod internal pressure. The occurrence of this failure mode might be related to the ductility remained in the M5
cladding was conducted at the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Although the transient signals obtained during the pulse-irradiation test did not show any signs of the occurrence of PCMI failure, the failure of the test fuel rod was confirmed from the visual inspection carried out after test CN-1. Analyses using fuel performance codes FEMAXI-8 and RANNS were also performed in order to investigate the fuel behavior during normal operation and pulse-irradiation regarding the test fuel rod of CN-1, and the results were consistent with this observation result. These experimental and calculation results suggested that the failure of test fuel rod of CN-1 was not caused by hydride-assisted PCMI but high-temperature rupture following the increase in rod internal pressure. The occurrence of this failure mode might be related to the ductility remained in the M5 cladding owing to its low content of the hydrogen absorbed during normal operation.
cladding owing to its low content of the hydrogen absorbed during normal operation.
湯村 尚典; 天谷 政樹
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 120, p.798 - 804, 2018/10
被引用回数:6 パーセンタイル:52.24(Nuclear Science & Technology)To investigate the relationship between the fracture resistance of a cladding tube and the amount of deformation of the cladding tube due to ballooning and rupture during a loss-of-coolant accident (LOCA), four-point-bending tests were performed using non-irradiated Zircaloy-4 cladding tubes which experienced a LOCA-simulated sequence (ballooning, rupture, high temperature oxidation and quench). According to the obtained results, it was found that the maximum bending stress of the cladding tube after the LOCA-simulated sequence, which was defined as the fracture resistance, correlated to the average thickness of prior- layer in the cladding tube. Based on the average thickness of prior-
layer in the cladding tube. Based on the average thickness of prior- layer, the fracture resistance of the cladding tube with ballooning and rupture was expressed as functions of isothermal oxidation time and temperature and the maximum circumferential strain on the cladding tube.
layer, the fracture resistance of the cladding tube with ballooning and rupture was expressed as functions of isothermal oxidation time and temperature and the maximum circumferential strain on the cladding tube.
菅原 隆徳; 辻本 和文
JAEA-Research 2017-011, 35 Pages, 2017/10
J-PARCで建設を計画している核変換物理実験施設(TEF-P)では、崩壊熱の高いマイナーアクチノイド(MA)含有量の高い燃料を強制冷却風で冷却しながら使用することを検討している。冷却用の空気が停止した場合、MA燃料の崩壊熱により燃料の最高温度が数百 Cに達すると評価しているが、その際のMA燃料被覆管材料の健全性を評価するデータが存在しなかった。そこで、TEF-Pでの使用条件を考慮した条件で被覆管破裂試験を行い、あわせてクリープ破断時間の評価を行うことで暫定的な制限温度の設定を目指した。被覆管破裂試験およびクリープ破断時間の評価結果から、600
Cに達すると評価しているが、その際のMA燃料被覆管材料の健全性を評価するデータが存在しなかった。そこで、TEF-Pでの使用条件を考慮した条件で被覆管破裂試験を行い、あわせてクリープ破断時間の評価を行うことで暫定的な制限温度の設定を目指した。被覆管破裂試験およびクリープ破断時間の評価結果から、600 C以下であれば、TEF-P用MA燃料被覆管の破損を防ぐことが可能であることを示した。以上から、TEF-P炉心の事故時における暫定的な被覆管最高温度を600
C以下であれば、TEF-P用MA燃料被覆管の破損を防ぐことが可能であることを示した。以上から、TEF-P炉心の事故時における暫定的な被覆管最高温度を600 Cと設定した。
Cと設定した。
成川 隆文; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(11), p.1758 - 1765, 2016/11
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:67.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the effect of azimuthal temperature distribution on the ballooning and rupture behavior of Zircaloy-4 (Zry-4) cladding tube, laboratory-scale experiments on non-irradiated Zry-4 cladding tube specimens were performed under transient-heating conditions which simulate loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) conditions by using an external heating method, and the data obtained were compared to those from a previous study where an internal heating method was used. The maximum circumferential strains ( s) of the cladding tube specimens were firstly divided by the engineering hoop stress (
s) of the cladding tube specimens were firstly divided by the engineering hoop stress ( ). The divided maximum circumferential strains,
). The divided maximum circumferential strains,  s, of the previous study, which used the internal heating method, were then corrected based on the azimuthal temperature difference (ATD) in the cladding tube specimen. The
s, of the previous study, which used the internal heating method, were then corrected based on the azimuthal temperature difference (ATD) in the cladding tube specimen. The  s for the external heating method which was used in this study agreed fairly well with the corrected
s for the external heating method which was used in this study agreed fairly well with the corrected  s obtained in the previous study which employed the internal heating method in the burst temperature range below
s obtained in the previous study which employed the internal heating method in the burst temperature range below  1200 K. Also, the area of rupture opening tended to increase with increasing of the value which is defined as
1200 K. Also, the area of rupture opening tended to increase with increasing of the value which is defined as  multiplied by
multiplied by  . From the results obtained in this study, it was suggested that
. From the results obtained in this study, it was suggested that  and the size of rupture opening of a cladding tube under LOCA-simulated conditions can be estimated mainly by using
and the size of rupture opening of a cladding tube under LOCA-simulated conditions can be estimated mainly by using  ,
,  and ATD in the cladding tube specimen, irrespective of heating methods.
and ATD in the cladding tube specimen, irrespective of heating methods.
成川 隆文; 天谷 政樹
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(1), p.112 - 122, 2016/01
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:54.81(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the effect of oxidation and crystal phase condition on the ballooning and rupture behaviors of cladding tube under simulated loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) conditions, laboratory-scale experiments were performed in which internally pressurized non-irradiated Zircaloy-4 (Zry-4) cladding specimens were heated to burst in steam and argon gas conditions. Values of the maximum circumferential strain were normalized by dividing them by engineering hoop stress at the time of rupture. The dependence of the normalized value on burst temperature and the relationship between the normalized value and the length, width and area of rupture opening were evaluated. The correlation between the normalized value and the burst temperature suggested that the fraction of the  phase in Zry-4 cladding specimens affected the strain in the specimens and the oxidation of specimens suppressed the amount of ballooning of the specimens. The relationship between the normalized value and the length, width and area of rupture opening indicated that the length, width and area of rupture opening depended on the crystal phase condition in Zry-4 cladding specimens irrespective of atmosphere in the case of the heating rate of
phase in Zry-4 cladding specimens affected the strain in the specimens and the oxidation of specimens suppressed the amount of ballooning of the specimens. The relationship between the normalized value and the length, width and area of rupture opening indicated that the length, width and area of rupture opening depended on the crystal phase condition in Zry-4 cladding specimens irrespective of atmosphere in the case of the heating rate of  3 K/s.
3 K/s.
本間 功三*; 石島 清見; 藤城 俊夫
JAERI-M 92-044, 322 Pages, 1992/04
NSRR計画では、これまでの未照射燃料を用いた実験に引続き、照射済燃料を用いた実験を進めている。本報告書は、NSRR照射済燃料実験と比較対照される海外照射済燃料RIA実験(SPERT及びPBF実験)の燃料破損挙動に関する知見を整理見直したものである。その結果、従来の未照射燃料実験とは異なる破損形態が認められた。即ち、SPERTでは、被覆管ふくれ破損とPCMI破損、PBFでは、PCMI破損であった。被覆管ふくれ破損は、予備照射中のFPガス放出やパルス照射時のFPガス放出と関連があると思われる。SPERT実験においてPCMIにより低発熱量時(85cal/y)に破損した燃料棒の破損原因は、予備照射中の過大な燃料棒腐食に伴う被覆管の脆化に起因していると思われる。また、一般的な照射済燃料の反応度事故時において想定される破損メカニズムと影響因子の関係を評価した。
古田 照夫; 上塚 寛; 川崎 了; 星野 昭; 磯 修一
JAERI-M 8497, 27 Pages, 1979/10
軽水炉冷却材過失事故時に生ずる内面酸化でジルカロイ被覆管に水素が吸収される。この水素吸収に関して、燃料棒の破裂/酸化試験およびジルカロイ管の滞留水蒸気あるいは水蒸気/水素混合雰囲気中の酸化試験によって検討を加えた。水素吸収は水蒸気/水素混合雰囲気中の水素の割合に依存して950 C以上の酸化で起る。そして、酸化時間が長くなるにつれて水素吸収量は増加する。このとき形成される酸化膜には単斜晶と混在した正方晶ジルコニアが比較的高い水素吸収量をもつ試料で認められる。燃料棒の水素吸収の場合、酸化の激しいところで発生した水素は水素吸収が容易に起る他の場所で吸収されるから、水素吸収は破裂開口の大きさや外側の水蒸気流速に影響される。
C以上の酸化で起る。そして、酸化時間が長くなるにつれて水素吸収量は増加する。このとき形成される酸化膜には単斜晶と混在した正方晶ジルコニアが比較的高い水素吸収量をもつ試料で認められる。燃料棒の水素吸収の場合、酸化の激しいところで発生した水素は水素吸収が容易に起る他の場所で吸収されるから、水素吸収は破裂開口の大きさや外側の水蒸気流速に影響される。
成川 隆文
no journal, ,
JAEA has conducted studies on fuel behaviors under loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) conditions with both unirradiated and high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tubes. As a result, various kinds of information have been obtained on behaviors of these cladding tubes under LOCA conditions: oxidation, ballooning and rupture, thermal shock resistance (fracture/non-fracture conditions), post-LOCA mechanical strength, etc. In addition, new LOCA tests are planned at JAEA for the purpose of investigating effects of phenomena of fuel fragmentation, relocation and dispersal (FFRD) on fuel behaviors and coolability of reactor core during LOCA. It is expected that these results including those obtained by the future study provide necessary information for future regulation on high-burnup fuels with advanced cladding alloys.
成川 隆文
no journal, ,
JAEA has conducted studies on fuel behaviors under loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) conditions with both unirradiated and high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tube materials. As a result, various kinds of information have been obtained on behaviors of these cladding tube materials under LOCA conditions: oxidation, ballooning, rupture, thermal shock resistance (fracture/non-fracture conditions), post-LOCA mechanical strength, etc. In addition, new LOCA tests are planned at JAEA for the purpose of investigating effects of phenomena of fuel fragmentation, relocation and dispersal (FFRD) on fuel behaviors and coolability of reactor core during a LOCA. It is expected that these results including those obtained by the future study provide necessary information for future regulation on high-burnup fuels with advanced cladding alloys.
成川 隆文
no journal, ,
JAEA has carried out studies on fuel behaviors under loss-of-coolant-accident (LOCA) conditions with both unirradiated and high-burnup advanced fuel cladding tube materials. As a result, various kinds of information have been obtained: oxidation, ballooning, rupture, thermal shock resistance (fracture/non-fracture conditions), post-LOCA mechanical strength, etc. In addition, new LOCA tests are planned at JAEA to investigate the effects of the phenomena of fuel fragmentation, relocation and dispersal (FFRD) on the fuel behaviors and the coolability of the reactor core during a LOCA. These results, including those obtained from the future study, are expected to provide the necessary information for future regulation on high-burnup fuels with advanced cladding alloys.